Embedded systems laboratory
The device was designed, programmed and made by computer science graduate Adam Słodki as part of an thesis entitled “Design and implantation of a wireless sensor network”.
Smart terrarium.
The device was designed, programmed and made by computer science graduate Filip Glapiński as part of his thesis entitled “Smart Terrarium”.
Design and implementation of the device control system.
The device was designed, programmed and made by an IT graduate Mateusz Wróbel as part of his thesis entitled “Design and implantation of a device control system”.
Design, software and implementation of the printing device in unusual materials
The device was designed, programmed and made by computer science graduate Krystian Kmieciak as part of his engineering thesis entitled “Design and implementation of a printing device in unusual materials”.
Smart house – design and implementation of the electrical devices control system
The smart house project was made by computer science graduate Adrian Lipowski. Smart home was the subject of an engineering thesis entitled “Smart home – design and implementation of a control system for electrical devices”.
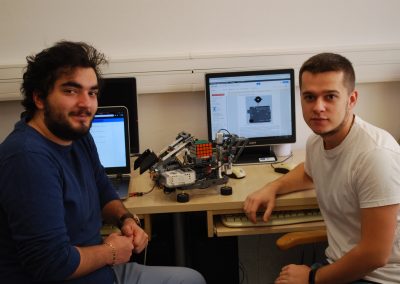
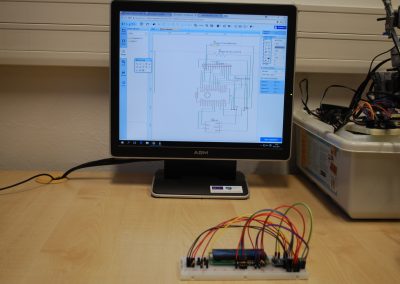
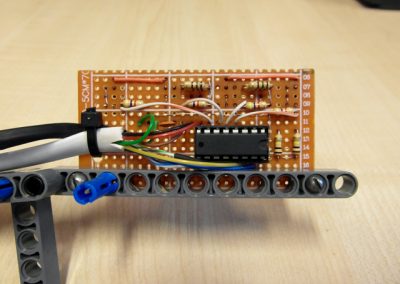
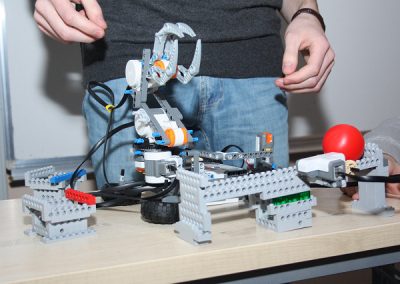
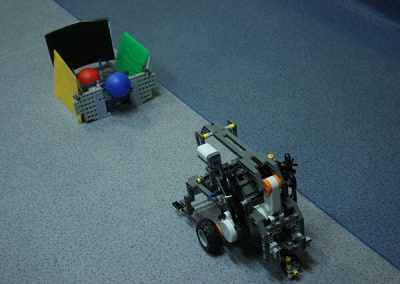
The design and implementation of the game using the microcontroller-controlled Lego NXT set
The design and implementation of the game using the microcontroller-controlled Lego NXT set was made by computer science graduate Adam Huńka. The design was made as part of an thesis.
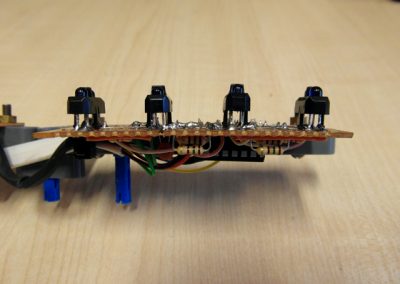
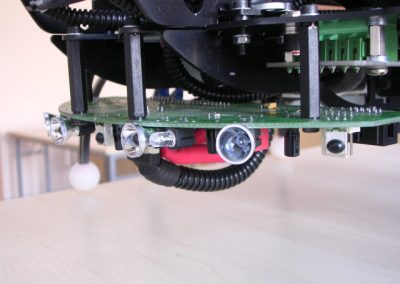
Sonar (ultrasonic distance sensor): the transmitter and receiver are placed at the end of the tail above the camera, this system returns the approximate distance from the nearest object, of course the sound-absorbing surfaces are invisible to it.
Whiskers (touch sensors): placed on the front of the robot sends an impulse when “touched”, and thus physical contact with the obstacle, unlike sonar works on any surface.Infrared (proximity) sensors: 1 on the front, up to 4 on the back (due to the lack of touch sensors in parts reviews). With this set you can control the robot using the TV remote control.The motherboard has a communication module, a serial radio link with a transmission speed of up to 78 kbps, using it we can communicate with the robot wirelessly by issuing commands from the computer.An analog camera is placed on the tail head. It is independent of the rest of the components and has its own antenna (2.4GHz), the image from it can also be viewed on a computer monitor screen.